Watts to Horsepower (Mechanical) Calculator
VerifiedConvert watts to horsepower with accuracy, learn the history and science behind power measurement
Power Calculator
Convert between different power units instantly with precise calculations
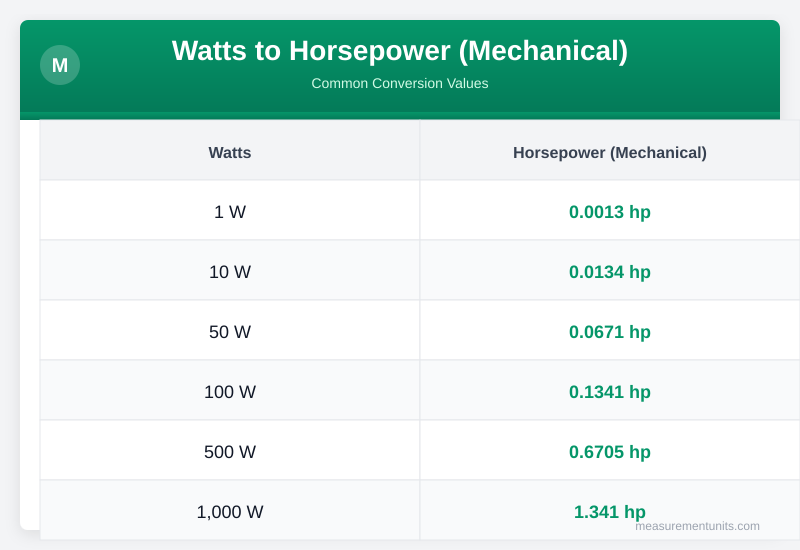
Watts to Horsepower (Mechanical) Conversion Table
Common Watts to Horsepower (Mechanical) conversion values
| Watts | Horsepower (Mechanical) |
|---|---|
| 1 W | 0.001 hp |
| 10 W | 0.013 hp |
| 50 W | 0.067 hp |
| 100 W | 0.134 hp |
| 500 W | 0.671 hp |
| 1000 W | 1.341 hp |
About Watts to Horsepower (Mechanical) Conversion
Watt and Horsepower measure the same thing differently. This tool bridges the gap so you don't have to do the math yourself.
The concept of measuring power dates back to the late 18th century when James Watt, a Scottish engineer, introduced the term 'horsepower' as a way to describe the power of steam engines in terms of the number of horses they could replace. This was a groundbreaking innovation, as it allowed for a standardized way to compare the power output of different machines. Today, we use both watts and horsepower to measure power, with watts being the SI unit for electrical power and horsepower being a more traditional unit often used in mechanical and automotive contexts.
The distinction between mechanical and electrical power is crucial when understanding the difference between watts and horsepower. Mechanical power refers to the rate at which work is done by a mechanical system, such as an engine or a machine, and is often measured in horsepower. Electrical power, on the other hand, refers to the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit and is measured in watts.
Understanding this difference is key to accurately converting between the two units. Engine ratings, particularly in the automotive industry, often use horsepower as a measure of power output. 7 watts.
However, modern engines and machines have power outputs that far exceed the original definition, making the conversion between watts and horsepower a common necessity. For instance, a typical passenger car engine might produce around 150 horsepower, which is equivalent to approximately 111,900 watts. The accuracy of converting watts to horsepower depends on the conversion factor used.
7. This conversion is not only useful for comparing the power output of different machines but also for understanding efficiency and performance metrics in various applications, including electrical systems, automotive engineering, and industrial equipment operation. For example, knowing the power consumption of an electrical motor in watts can help determine its equivalent horsepower rating, which is crucial for selecting the appropriate motor for a specific task or application.
The history of power measurement and conversion has evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in technology leading to more precise and efficient methods for calculating and comparing power outputs. Today, conversions between watts and horsepower are not only a matter of historical interest but also of practical importance in a wide range of fields, from renewable energy systems to industrial manufacturing processes. Understanding these conversions can provide valuable insights into system performance, efficiency, and potential areas for improvement, making it a fundamental aspect of engineering and technical disciplines.
Conversion Methods
7 watts (W). 7. 71 hp.
There are multiple methods to perform this conversion, including using a calculator or a conversion chart. However, understanding the step-by-step process is essential for ensuring accuracy and for being able to perform conversions without relying on external tools. 41 horsepower.
Approximation techniques can also be useful for quick mental math conversions. For example, knowing that 1 horsepower is roughly equal to 746 watts allows for rapid estimations. 02 horsepower.
While this method is less precise than the exact conversion, it can be helpful for scenarios where an approximate value is sufficient. Precision matters in many applications, especially in engineering and industrial contexts where small differences in power output can significantly impact system performance and efficiency. 7 watts per horsepower is crucial.
For example, when designing an electrical system, accurately converting the total power consumption from watts to horsepower can help in selecting the appropriate size and type of equipment, such as generators or motors. Common mistakes to avoid during conversions include using incorrect conversion factors or failing to account for the context of the measurement. For instance, if the wattage includes a mention of 'watt-hours' (a unit of energy), it must first be converted to watts (a unit of power) before being converted to horsepower.
Another mistake is not considering the efficiency of the system, as real-world applications often involve losses that affect the actual power output. For example, an electrical motor might have an efficiency rating of 90%, meaning that 10% of the input power is lost as heat, which should be accounted for when calculating the equivalent horsepower. Mental math shortcuts can be developed with practice, allowing for quick conversions without the need for a calculator.
34) can be useful for quick estimations. Similarly, knowing that doubling the wattage will double the horsepower output can help in making rapid calculations.
Practical Applications
The conversion between watts and horsepower has numerous practical applications across various fields. In electrical systems, knowing the power consumption in watts and being able to convert it to horsepower is essential for designing and operating systems efficiently. For example, when planning the installation of a new electrical motor, converting its power rating from watts to horsepower can help in determining the appropriate capacity of the electrical supply and in ensuring that the motor can meet the required performance specifications.
Automotive performance is another area where the conversion between watts and horsepower is critical. Car manufacturers often advertise the horsepower of their vehicles, which is a direct measure of the engine's power output. However, when comparing the performance of electric vehicles (which are often rated in watts or kilowatts) to traditional gasoline-powered cars, converting the electrical power to horsepower provides a common basis for comparison.
7 watts/hp ≈ 201 hp). Industrial equipment and machinery also rely on accurate power measurements and conversions. In manufacturing processes, understanding the power requirements of different machines in both watts and horsepower is crucial for ensuring that systems are properly sized and configured.
This not only helps in optimizing performance but also in minimizing energy waste and reducing operational costs. For example, a factory might use machinery with power ratings in horsepower for some tasks and others rated in watts for different applications, necessitating conversions to manage and compare their energy usage effectively. Renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines and solar panels, generate power that is often measured in watts or kilowatts.
When integrating these systems into the grid or comparing their performance to traditional fossil-fuel-based power plants, converting their electrical power output to horsepower can provide a useful metric for evaluation. This conversion helps in understanding the scale and impact of renewable energy sources in the context of overall energy production and consumption. Efficiency ratings of systems and devices are also closely related to power measurements and conversions.
Understanding how much power a device consumes (in watts) and being able to convert this to its equivalent horsepower can provide insights into its efficiency and performance. For example, a highly efficient motor might consume fewer watts to produce the same horsepower as a less efficient model, making the conversion between watts and horsepower a valuable tool for comparing and selecting equipment based on energy efficiency and performance criteria.
Watts to Horsepower (Mechanical) Conversion Chart