Kilowatt Hours to Kilocalories Calculator
VerifiedLearn to convert kilowatt hours to kilocalories with precision and understand the importance of energy unit conversions in various fields.
Energy Calculator
Convert between different energy units instantly with precise calculations
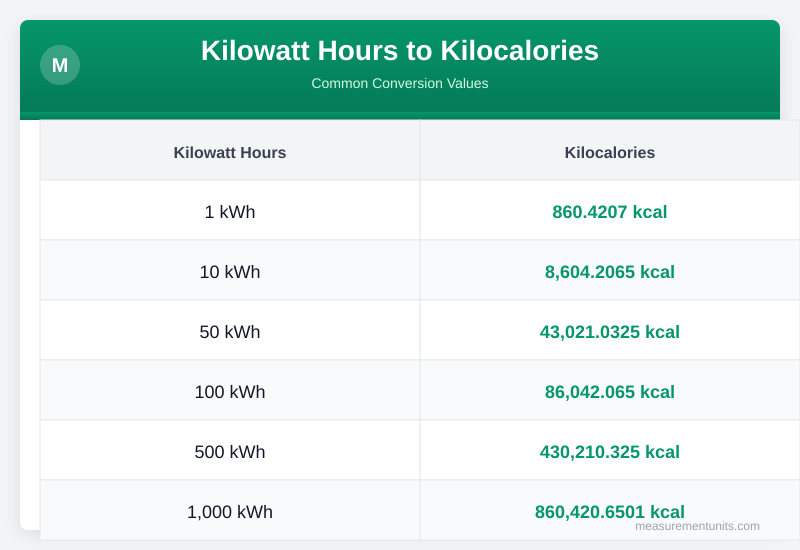
Kilowatt Hours to Kilocalories Conversion Table
Common Kilowatt Hours to Kilocalories conversion values
| Kilowatt Hours | Kilocalories |
|---|---|
| 1 kWh | 860.421 kcal |
| 10 kWh | 8604.207 kcal |
| 50 kWh | 43021.033 kcal |
| 100 kWh | 86042.065 kcal |
| 500 kWh | 430210.325 kcal |
| 1000 kWh | 860420.650 kcal |
About Kilowatt Hours to Kilocalories Conversion
Converting Kilowatt Hour to Kilocalorie is simple: just use the calculator above. If you want to understand the math or do it by hand, keep reading.
The evolution of energy units has been a long and winding road, with various civilizations contributing to our understanding of energy and its measurement. From the early days of mechanical energy, where the watt was defined in terms of the horsepower, to the modern era of electrical energy, where the kilowatt hour (kWh) reigns supreme, our comprehension of energy has become increasingly sophisticated. The kilocalorie (kcal), a unit of thermal energy, has its roots in the early 19th century, when scientists like Sadi Carnot and Rudolf Clausius laid the groundwork for the study of thermodynamics.
Understanding the difference between mechanical and thermal energy is crucial, as it forms the basis of efficiency calculations in various fields, such as engineering and physics. For instance, a typical incandescent light bulb has an efficiency of around 2-3%, meaning that only 2-3% of the electrical energy consumed is converted into visible light, while the rest is lost as heat. The conversion from kilowatt hours to kilocalories is not just a matter of multiplying by a conversion factor, but also understanding the underlying principles of energy transformation.
421 kcal, which is derived from the definitions of the two units. This conversion factor is essential in calculating the efficiency of various systems, such as power plants, where the energy output in kilocalories is compared to the energy input in kilowatt hours. For example, a power plant with an efficiency of 30% would produce 300 kcal of thermal energy for every 1000 kWh of electrical energy input.
In many applications, such as utility billing and nutrition labeling, precise conversions are crucial to ensure accuracy and fairness. In the case of utility billing, the conversion from kWh to kcal is used to calculate the energy consumed by households and industries, which in turn affects the billing amounts. In nutrition labeling, the conversion from kcal to other units like joules or BTUs is necessary to provide consumers with accurate information about the energy content of food products.
The precision of these conversions is essential, as small errors can add up over time, leading to significant discrepancies. The history of energy unit conversions is also noteworthy, as it reflects the development of human understanding of energy and its various forms. The concept of energy itself was not well-defined until the 19th century, when the law of conservation of energy was formulated.
Since then, our understanding of energy has expanded to include various forms, such as kinetic energy, potential energy, thermal energy, and more. The development of new energy units and conversion factors has been an ongoing process, with each new discovery and innovation leading to a deeper understanding of the complex relationships between different forms of energy. In conclusion, the conversion from kilowatt hours to kilocalories is an essential process that underlies many applications in various fields.
By understanding the evolution of energy units, the difference between mechanical and thermal energy, and the importance of precision in conversion calculations, we can appreciate the significance of this conversion and its impact on our daily lives.
Conversion Methods
The conversion from kilowatt hours to kilocalories can be performed using various methods, each with its own advantages and limitations. 421 kcal, which is derived from the definitions of the two units. This conversion factor can be used to calculate the energy in kilocalories for a given amount of energy in kilowatt hours.
5 kcal. 006 kcal. This method is useful when working with large amounts of energy, as it avoids the need to deal with very large or very small numbers.
421 kcal/MWh = 20,670,096 kcal. In addition to these methods, there are also approximation techniques and mental math shortcuts that can be used to estimate the conversion from kilowatt hours to kilocalories. One such technique is to use the approximate conversion factor of 1 kWh ≈ 860 kcal, which is close enough for many purposes.
6 megajoules, and then use the conversion factor 1 MJ ≈ 239 kcal to estimate the energy in kilocalories. These approximation techniques are useful when a high degree of precision is not required, such as in rough estimates or order-of-magnitude calculations. However, it's essential to note that precision matters in many applications, and using approximate conversion factors or mental math shortcuts can lead to significant errors.
For example, in utility billing, small errors in energy calculations can add up over time, leading to discrepancies in billing amounts. In nutrition labeling, precise conversions are necessary to provide consumers with accurate information about the energy content of food products. Therefore, it's crucial to use the exact conversion factor or precise calculation methods when accuracy is critical.
Common conversion mistakes to avoid include using incorrect conversion factors, such as 1 kWh = 1000 kcal, or failing to account for the differences between mechanical and thermal energy. Another mistake is to assume that the conversion from kilowatt hours to kilocalories is always exact, when in fact it depends on the specific context and application.
Practical Applications
The conversion from kilowatt hours to kilocalories has numerous applications in various fields, including utility billing, nutrition labeling, industrial processes, and renewable energy. In utility billing, the conversion is used to calculate the energy consumed by households and industries, which affects the billing amounts. 5 kcal.
In nutrition labeling, the conversion is used to provide consumers with accurate information about the energy content of food products. Food manufacturers use the conversion factor to calculate the energy content of their products in kilocalories, which is then displayed on the nutrition label. 116 kWh per serving, which can be calculated using the conversion factor.
Industrial processes, such as power generation and transmission, rely heavily on the conversion from kilowatt hours to kilocalories. Power plants use the conversion to calculate their energy output in kilocalories, which is then compared to the energy input in kilowatt hours to determine the plant's efficiency. For example, a power plant with an efficiency of 30% would produce 300 kcal of thermal energy for every 1000 kWh of electrical energy input.
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, also rely on the conversion from kilowatt hours to kilocalories. The energy output of solar panels and wind turbines is typically measured in kilowatt hours, which is then converted to kilocalories to determine the thermal energy equivalent. This conversion is essential in evaluating the performance and efficiency of renewable energy systems.
Efficiency calculations are another critical application of the conversion from kilowatt hours to kilocalories. By comparing the energy output in kilocalories to the energy input in kilowatt hours, engineers and researchers can evaluate the efficiency of various systems, such as engines, motors, and power plants. For instance, a car engine with an efficiency of 25% would convert 25% of the energy in the fuel into useful work, while the remaining 75% is lost as heat.
In conclusion, the conversion from kilowatt hours to kilocalories is a fundamental process that underlies many applications in various fields.
Kilowatt Hours to Kilocalories Conversion Chart