Horsepower (Mechanical) to Kilowatts Calculator
VerifiedConvert horsepower to kilowatts with our easy-to-use tool and learn about power measurement history, conversion accuracy, and applications.
Power Calculator
Convert between different power units instantly with precise calculations
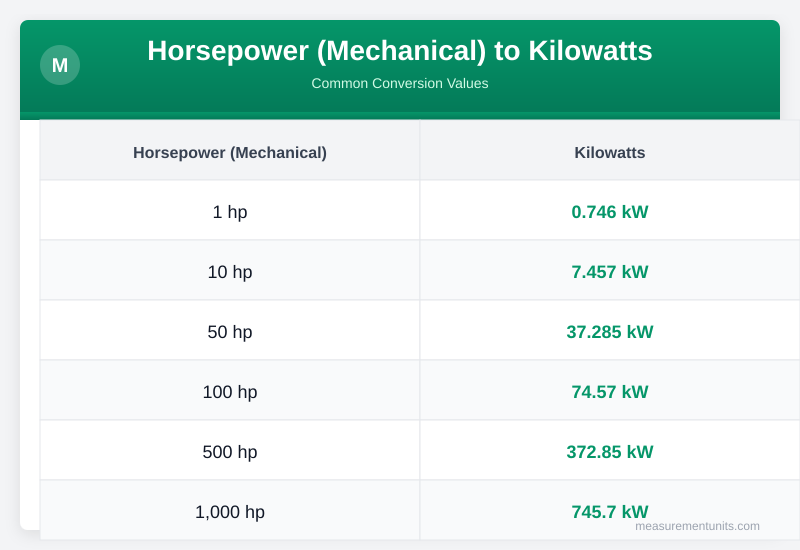
Horsepower (Mechanical) to Kilowatts Conversion Table
Common Horsepower (Mechanical) to Kilowatts conversion values
| Horsepower (Mechanical) | Kilowatts |
|---|---|
| 1 hp | 0.746 kW |
| 10 hp | 7.457 kW |
| 50 hp | 37.285 kW |
| 100 hp | 74.570 kW |
| 500 hp | 372.850 kW |
| 1000 hp | 745.700 kW |
About Horsepower (Mechanical) to Kilowatts Conversion
Need to convert Horsepower to Kilowatt? Enter your value above for an instant answer. Below, we break down how the conversion works and when you'll need it.
The concept of measuring power dates back to the late 18th century when James Watt, a Scottish engineer, introduced the term 'horsepower' as a way to describe the power of steam engines. Initially, one horsepower was equivalent to the power required to lift 33,000 pounds by one foot in one minute. Today, horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement for power, primarily used in the context of engines, motors, and other machines, while the kilowatt (kW) is the SI unit of power, used in electrical and mechanical engineering.
Mechanical power, such as that produced by an engine, and electrical power, such as that generated by a generator, are two different forms of energy. Mechanical power is typically measured in horsepower, while electrical power is measured in kilowatts. Understanding the relationship between these two units is crucial in various fields, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial engineering.
For instance, when designing an electric vehicle, engineers need to convert the horsepower of the vehicle's engine to kilowatts to determine its electrical power output. Engine ratings, such as those found in automotive and industrial applications, often involve horsepower measurements. For example, a car's engine might be rated at 200 horsepower, while a wind turbine might be rated at 2,000 kilowatts.
To compare these values, it's necessary to perform a conversion between horsepower and kilowatts. 7457 kilowatts. 14 kilowatts.
The accuracy of horsepower to kilowatt conversions is critical in various applications, including electrical systems, automotive performance, and industrial equipment. Small errors in conversion can result in significant discrepancies in calculated values, leading to inefficiencies, safety hazards, or equipment damage. For instance, if an engineer underestimates the power output of a generator by 10%, it may not be able to meet the required load, causing power outages or equipment failure.
The history of power measurement has evolved significantly since James Watt's time. With the advent of electrical power, the need for accurate conversions between mechanical and electrical power units has become increasingly important.
Conversion Methods
7457 kilowatts. This value can be applied using various calculation methods, including multiplication, division, and proportion. 85 kilowatts.
Step-by-step examples can help illustrate the conversion process. Suppose we want to convert 250 horsepower to kilowatts. 7457 kilowatts.
43 kilowatts. Approximation techniques can be useful when performing mental math or estimating values. 75, which is close enough for rough estimates.
75). Mental math shortcuts can also be helpful when dealing with common conversion values. 57 kilowatts, making it easier to convert values like 200 or 500 horsepower.
7457. 75 can be sufficient. It's crucial to avoid common conversion mistakes, such as using an incorrect conversion factor or failing to account for unit conversions.
For instance, if we forget to convert hours to seconds when calculating power, we may end up with incorrect results. To demonstrate the importance of precision, consider the example of a 1,000-horsepower engine. 7 kilowatts.
4% error.
Practical Applications
The conversion of horsepower to kilowatts has numerous practical applications across various fields. In electrical systems, understanding the relationship between mechanical and electrical power is crucial for designing and optimizing power generation, transmission, and distribution systems. For instance, when sizing a generator for a data center, engineers need to convert the required mechanical power to electrical power to ensure the generator can meet the load.
In automotive performance, horsepower to kilowatt conversions are essential for evaluating a vehicle's acceleration, top speed, and fuel efficiency. By converting a car's horsepower to kilowatts, drivers can better understand its electrical power output and optimize their driving habits. For example, a driver may want to know the kilowatt equivalent of their car's 300-horsepower engine to determine its electrical power output when connected to an external generator.
Industrial equipment, such as pumps, compressors, and conveyor belts, often require precise power calculations to ensure efficient operation and safety. By converting horsepower to kilowatts, engineers can optimize equipment design, reduce energy consumption, and improve overall system performance. For instance, a manufacturing plant may use a 500-horsepower pump to drive its operations.
85 kilowatts), the plant's engineers can better understand its electrical power requirements and optimize its energy usage. Renewable energy systems, such as wind and solar power, rely on accurate power conversions to determine their efficiency and output. By converting the mechanical power of a wind turbine to kilowatts, engineers can evaluate its electrical power output and optimize its performance.
For example, a 2,000-kilowatt wind turbine is equivalent to approximately 2,683 horsepower, demonstrating the importance of accurate conversions in renewable energy applications. Efficiency ratings, such as those used in energy-efficient appliances and machinery, often involve horsepower to kilowatt conversions. By understanding the relationship between mechanical and electrical power, manufacturers can optimize their designs, reduce energy consumption, and improve overall system performance.
1864 kilowatts.
Horsepower (Mechanical) to Kilowatts Conversion Chart