Kilogram Meters to Newton Meters Calculator
VerifiedEasily convert kilogram meters to newton meters with our expert guide, covering rotational force measurement and precision applications
Torque Calculator
Convert between different torque units instantly with precise calculations
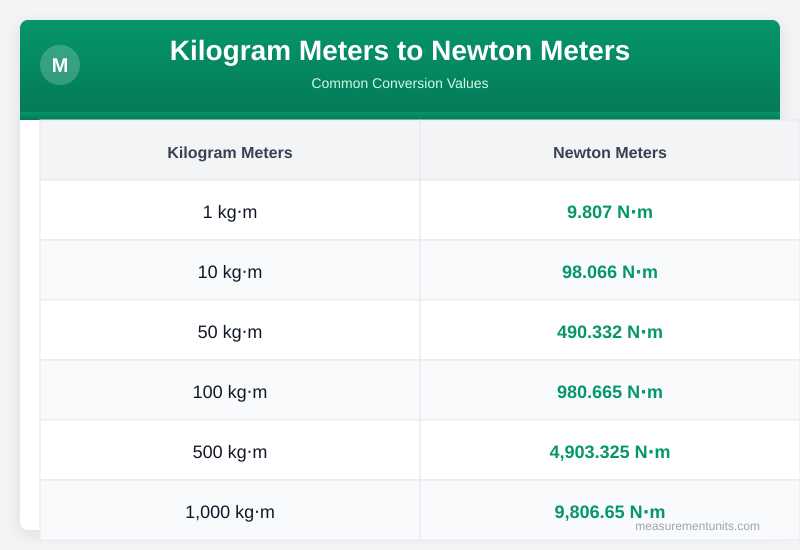
Kilogram Meters to Newton Meters Conversion Table
Common Kilogram Meters to Newton Meters conversion values
| Kilogram Meters | Newton Meters |
|---|---|
| 1 kg⋅m | 9.807 N⋅m |
| 10 kg⋅m | 98.066 N⋅m |
| 50 kg⋅m | 490.332 N⋅m |
| 100 kg⋅m | 980.665 N⋅m |
| 500 kg⋅m | 4903.325 N⋅m |
| 1000 kg⋅m | 9806.650 N⋅m |
About Kilogram Meters to Newton Meters Conversion
Need to convert Kilogram Meter to Newton Meter? Enter your value above for an instant answer. Below, we break down how the conversion works and when you'll need it.
The kilogram-meter and newton-meter are units of measurement for rotational force, or torque, which is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering. The study of torque dates back to the work of Archimedes, who first described the principle of mechanical advantage in the 3rd century BC. Today, understanding torque is crucial in a wide range of applications, from automotive mechanics to industrial machinery and robotics.
In these contexts, precise measurement and conversion of torque units are essential for ensuring safety, efficiency, and optimal performance.
In mechanical systems, torque is used to generate rotational motion or to apply a twisting force to an object. The kilogram-meter is a unit of torque that represents the force required to rotate an object around a pivot point, with one kilogram-meter equivalent to the force exerted by a one kilogram mass at a distance of one meter from the pivot point. The newton-meter, on the other hand, represents the force required to rotate an object around a pivot point, with one newton-meter equivalent to the force exerted by a one newton force at a distance of one meter from the pivot point.
The need for precise torque measurement and conversion arises in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. For example, in automotive mechanics, the torque specification for a particular engine or transmission component must be carefully measured and controlled to ensure proper function and avoid damage. Similarly, in industrial machinery, the torque output of a motor or gearbox must be precisely matched to the requirements of the application to achieve optimal efficiency and productivity.
In these contexts, the ability to convert between kilogram-meters and newton-meters is essential for communicating specifications, comparing performance, and troubleshooting issues.
The importance of precision in torque measurement and conversion cannot be overstated. In many applications, even small errors in torque measurement or conversion can have significant consequences, including reduced efficiency, increased wear and tear, and even catastrophic failure. For example, in the aerospace industry, the torque specification for a critical component such as a rocket engine or satellite motor must be precisely controlled to ensure reliable operation and avoid potentially disastrous consequences.
Similarly, in the manufacturing industry, the torque output of a machine tool or robotic system must be carefully calibrated and controlled to produce high-quality products and avoid defects or damage.
To ensure precision and accuracy in torque measurement and conversion, it is essential to understand the underlying principles and units involved. The kilogram-meter and newton-meter are both derived from the International System of Units (SI), which provides a standardized framework for measurement and conversion. By mastering the conversion between these units, engineers and technicians can ensure that their designs and applications are optimized for performance, safety, and efficiency.
Conversion Methods
The conversion factor between kilogram-meters and newton-meters is based on the definition of the units. 80665 newtons (the force exerted by gravity on a one kilogram mass at sea level). 80665.
0665 newton-meters.
There are several methods for converting between kilogram-meters and newton-meters, including exact calculation, approximation, and mental math shortcuts. 80665. 16625 newton-meters.
81, which is close enough for many practical applications. 5 newton-meters.
In addition to exact calculation and approximation, there are several mental math shortcuts that can be used to quickly estimate the conversion between kilogram-meters and newton-meters. 8 newton-meters, a rough estimate can be made by multiplying the value in kilogram-meters by 10 and then subtracting 2%. For example, to convert 75 kilogram-meters to newton-meters, multiply 75 by 10 to get 750, and then subtract 2% (15) to get 735 newton-meters.
When precision matters, it is essential to use the exact conversion factor and to avoid common mistakes such as rounding or truncating the result. For example, in the aerospace industry, the torque specification for a critical component such as a rocket engine or satellite motor must be precisely controlled to ensure reliable operation and avoid potentially disastrous consequences. In such cases, the conversion between kilogram-meters and newton-meters must be made with the highest possible precision, using the exact conversion factor and avoiding any approximations or shortcuts.
Common conversion mistakes to avoid include rounding or truncating the result, using an incorrect conversion factor, and neglecting to account for units. For example, if a value is given in kilogram-meters but the units are not properly accounted for, the result may be incorrect or misleading. To avoid such mistakes, it is essential to carefully check the units and to use the exact conversion factor whenever possible.
Practical Applications
The conversion between kilogram-meters and newton-meters has numerous applications in various industries, including automotive mechanics, industrial machinery, robotics, and precision instruments. In automotive mechanics, the torque specification for a particular engine or transmission component must be carefully measured and controlled to ensure proper function and avoid damage. For example, the torque output of an engine crankshaft or transmission gearset must be precisely matched to the requirements of the application to achieve optimal efficiency and productivity.
In industrial machinery, the torque output of a motor or gearbox must be precisely matched to the requirements of the application to achieve optimal efficiency and productivity. For example, in a manufacturing plant, the torque output of a machine tool or robotic system must be carefully calibrated and controlled to produce high-quality products and avoid defects or damage. The conversion between kilogram-meters and newton-meters is essential in such applications, as it allows engineers and technicians to communicate specifications, compare performance, and troubleshoot issues.
In robotics, the torque output of a motor or actuator must be precisely controlled to achieve optimal performance and avoid damage. For example, in a robotic arm or gripper, the torque output of the motor must be carefully matched to the requirements of the application to achieve precise control and avoid slippage or overload. The conversion between kilogram-meters and newton-meters is essential in such applications, as it allows engineers and technicians to optimize the design and performance of the robotic system.
In precision instruments, the torque output of a motor or mechanism must be precisely controlled to achieve optimal performance and avoid damage. For example, in a scientific instrument such as a spectrometer or microscope, the torque output of the motor must be carefully matched to the requirements of the application to achieve precise control and avoid vibrations or distortions. The conversion between kilogram-meters and newton-meters is essential in such applications, as it allows engineers and technicians to optimize the design and performance of the instrument.
In mechanical engineering, the conversion between kilogram-meters and newton-meters is essential for designing and optimizing mechanical systems. For example, in the design of a gear train or bearing system, the torque output of the motor or mechanism must be carefully matched to the requirements of the application to achieve optimal efficiency and productivity. The conversion between kilogram-meters and newton-meters allows engineers and technicians to communicate specifications, compare performance, and troubleshoot issues, and is a critical part of the design and development process.
Kilogram Meters to Newton Meters Conversion Chart