Kilowatts to Horsepower (Mechanical) Calculator
VerifiedAccurately convert kilowatts to horsepower with our comprehensive guide and calculator
Power Calculator
Convert between different power units instantly with precise calculations
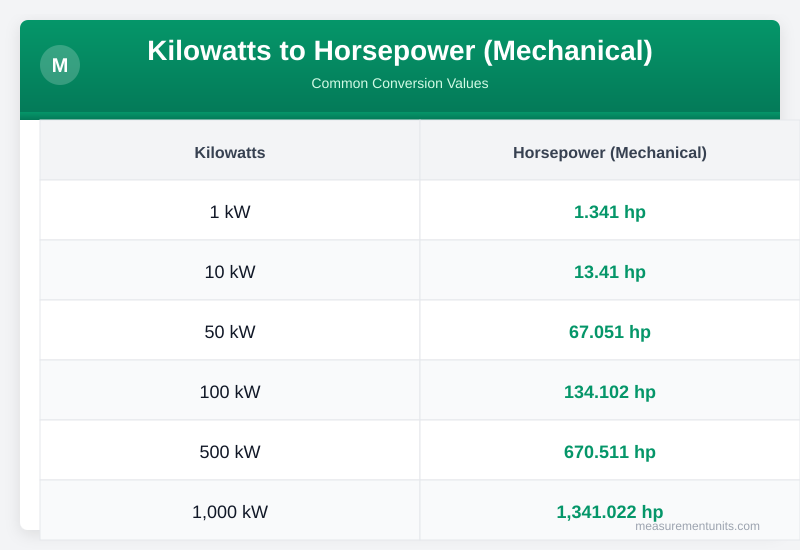
Kilowatts to Horsepower (Mechanical) Conversion Table
Common Kilowatts to Horsepower (Mechanical) conversion values
| Kilowatts | Horsepower (Mechanical) |
|---|---|
| 1 kW | 1.341 hp |
| 10 kW | 13.410 hp |
| 50 kW | 67.051 hp |
| 100 kW | 134.102 hp |
| 500 kW | 670.511 hp |
| 1000 kW | 1341.022 hp |
About Kilowatts to Horsepower (Mechanical) Conversion
Need to convert Kilowatt to Horsepower? Enter your value above for an instant answer. Below, we break down how the conversion works and when you'll need it.
The measurement of power has a rich history that dates back to the late 18th century when James Watt, a Scottish engineer, introduced the concept of horsepower (hp) as a unit of measurement for the power of steam engines. This unit was derived from the estimated power of a strong horse, which was calculated to be approximately 33,000 foot-pounds per minute. The development of electrical power systems in the 19th century led to the introduction of new units, including the watt (W) and its larger counterpart, the kilowatt (kW).
Understanding the differences between mechanical and electrical power is crucial for accurate conversions between these units. Mechanical power refers to the ability of a system to perform work, typically measured in horsepower, while electrical power is a measure of the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit, measured in watts or kilowatts.
In the context of engine ratings, horsepower is often used to express the power output of an internal combustion engine, whereas kilowatts are commonly used to express the power output of electrical motors or generators. The conversion between these units is essential for engineers, technicians, and operators who work with both mechanical and electrical systems. For instance, when specifying the power requirements of an electric motor to replace a diesel engine, or when calculating the energy consumption of an industrial process, accurate conversions between kilowatts and horsepower are critical.
The history of power measurement also highlights the importance of standardization. Today, the International System of Units (SI) defines the watt as the standard unit of power, with 1 watt being equal to 1 joule per second. 7 watts.
This conversion factor is essential for accurate calculations and is widely used in various fields, including electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, and automotive engineering.
The need for accurate conversions between kilowatts and horsepower arises from the diverse applications of these units. In electrical systems, kilowatts are used to specify the power capacity of generators, motors, and electrical distribution systems. In automotive performance, horsepower is often used to express the power output of an engine, while kilowatts are used in electric vehicles.
In industrial equipment, both units are used to specify the power requirements of machinery, such as pumps, fans, and conveyor belts. The conversion between kilowatts and horsepower is also crucial in renewable energy applications, where the power output of solar panels or wind turbines is often expressed in kilowatts, while the power requirements of electrical loads are expressed in horsepower.
In addition to the technical aspects of power measurement, understanding the historical context and standardization efforts is essential for appreciating the complexity of power conversions. The development of power measurement units has been shaped by the contributions of scientists and engineers over the centuries, and the standardization of these units has facilitated international trade, innovation, and cooperation. By recognizing the importance of accurate power conversions, we can better appreciate the intricate relationships between mechanical and electrical power, and the critical role that these conversions play in various industries and applications.
Conversion Methods
The exact conversion factor between kilowatts and horsepower is based on the definition of these units. 34102 horsepower (hp). This conversion factor can be used to calculate the horsepower equivalent of a given kilowatt value, or vice versa.
4102 hp.
There are multiple calculation methods to convert kilowatts to horsepower, each with its own advantages and limitations. The simplest method is to use the conversion factor, as shown in the previous example. Another method is to use a calculator or a computer program that can perform the conversion automatically.
For instance, many online calculators and conversion tools offer kilowatt-to-horsepower conversions, often with additional features such as unit selection and precision control. When working with large or complex calculations, it may be necessary to use specialized software or consulting services to ensure accurate results.
To illustrate the conversion process, let's consider a few examples. Suppose we want to convert 5 kW to horsepower. 7051 hp.
913 kW. These examples demonstrate the straightforward nature of the conversion process, which can be applied to a wide range of values and applications.
Approximation techniques can be useful when working with rough estimates or when precision is not critical. 3 horsepower. This approximation can be used for quick mental math calculations or for estimating the power requirements of a system.
However, it's essential to note that approximations can lead to errors, especially when working with large or complex systems. To minimize errors, it's recommended to use the exact conversion factor or to consult with a qualified professional.
Mental math shortcuts can be helpful for making quick estimates or conversions. 3 = hp. This shortcut is based on the approximate conversion factor and can be used for rough estimates.
However, for precise calculations, it's always best to use the exact conversion factor or to consult with a qualified professional. When precision matters, such as in critical engineering applications or high-stakes performance evaluations, it's essential to use the most accurate conversion methods available.
Common conversion mistakes to avoid include using incorrect conversion factors, rounding errors, and neglecting to consider the context of the conversion. For instance, if we are converting kilowatts to horsepower for an electrical motor, we need to ensure that we are using the correct conversion factor and that we are considering the efficiency of the motor. By being aware of these potential pitfalls, we can ensure accurate and reliable conversions that meet the needs of our specific application or use case.
Practical Applications
In electrical systems, kilowatts are used to specify the power capacity of generators, motors, and electrical distribution systems. For example, a residential electrical panel may be rated for 200 amps at 240 volts, which corresponds to a power capacity of approximately 48 kW. In contrast, a large industrial motor may be rated for 1,000 kW or more.
The conversion between kilowatts and horsepower is essential for ensuring that the electrical system can meet the power requirements of the mechanical loads.
In automotive performance, horsepower is often used to express the power output of an engine, while kilowatts are used in electric vehicles. For instance, a high-performance sports car may have an engine rated for 500 horsepower, which is equivalent to approximately 373 kW. In electric vehicles, the power output is typically expressed in kilowatts, such as a 150 kW electric motor.
The conversion between kilowatts and horsepower allows engineers to compare the performance of different vehicles and to optimize the design of their powertrains.
In industrial equipment, both kilowatts and horsepower are used to specify the power requirements of machinery, such as pumps, fans, and conveyor belts. 3 kW. In this context, the conversion between kilowatts and horsepower is essential for ensuring that the electrical system can meet the power requirements of the machinery.
By understanding the power requirements of their equipment, industrial operators can optimize their energy consumption, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
In renewable energy applications, the power output of solar panels or wind turbines is often expressed in kilowatts, while the power requirements of electrical loads are expressed in horsepower. 4 horsepower. The conversion between kilowatts and horsepower allows engineers to design and optimize renewable energy systems that can meet the power requirements of their loads.
By taking into account the efficiency of the system and the power requirements of the loads, engineers can create optimized solutions that minimize energy waste and maximize overall performance.
Efficiency ratings are another critical aspect of power conversions. In many applications, the efficiency of a system or component is expressed as a percentage, such as the efficiency of an electrical motor or the efficiency of a solar panel. By understanding the efficiency of a system, engineers can optimize the design and operation of the system to minimize energy losses and maximize overall performance.
The conversion between kilowatts and horsepower is essential for calculating the efficiency of a system, as it allows engineers to compare the power output of the system to the power requirements of the loads. By taking into account the efficiency of the system and the power requirements of the loads, engineers can create optimized solutions that minimize energy waste and maximize overall performance.
Kilowatts to Horsepower (Mechanical) Conversion Chart