Kilobytes to Megabytes Calculator
VerifiedConvert kilobytes to megabytes with ease, learn about binary systems, and understand storage precision
Data Size Calculator
Convert between different data size units instantly with precise calculations
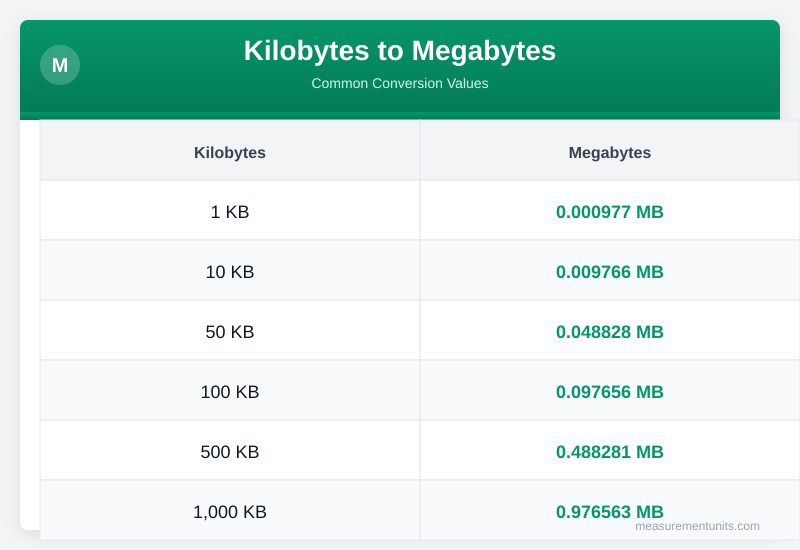
Kilobytes to Megabytes Conversion Table
Common Kilobytes to Megabytes conversion values
| Kilobytes | Megabytes |
|---|---|
| 1 KB | 0.001 MB |
| 10 KB | 0.010 MB |
| 50 KB | 0.049 MB |
| 100 KB | 0.098 MB |
| 500 KB | 0.488 MB |
| 1000 KB | 0.977 MB |
About Kilobytes to Megabytes Conversion
Need to convert Kilobyte to Megabyte? Enter your value above for an instant answer. Below, we break down how the conversion works and when you'll need it.
The conversion of kilobytes (KB) to megabytes (MB) is a fundamental process in the realm of digital information, rooted in the understanding of binary and decimal systems. Unlike the decimal system, which is based on powers of 10, the binary system used by computers operates on powers of 2. This discrepancy leads to slight differences in how storage sizes are represented and calculated.
For instance, while 1 kilobyte is often considered as 1,000 bytes in decimal terms, in binary, it equals 2^10, or 1,024 bytes. This distinction is crucial for accurate storage and data transfer calculations.
The evolution of computer storage has been a remarkable journey, from the early days of floppy disks that could hold mere kilobytes of data to the current era of terabyte-sized hard drives and cloud storage facilities. As technology advances and the demand for larger, faster storage solutions increases, the importance of precise data size conversions becomes more evident. For example, understanding that 1 megabyte is equal to 1,024 kilobytes (or 2^20 bytes) can significantly impact how data is managed, transferred, and stored, ensuring that systems operate efficiently and effectively.
Conversions between different units of digital information, such as from kilobytes to megabytes, matter profoundly in technology for several reasons. Firstly, they enable precise calculations of storage needs, ensuring that enough space is allocated for files, programs, and data without waste. Secondly, they facilitate the optimization of data transfer over networks, where bandwidth is a critical factor.
For instance, knowing that a file is 5 megabytes in size (approximately 5,120 kilobytes) can help in estimating download times and required network resources.
The precision in these conversions also plays a vital role in software development, where memory allocation and data processing are critical. Developers must accurately calculate the size of data structures and the amount of memory their applications will require to function correctly. In digital media, where files can range from a few kilobytes for simple text files to gigabytes for high-definition videos, understanding data sizes is essential for planning storage, managing downloads, and optimizing streaming services.
Historically, the development of standards for data measurement has helped in streamlining these conversions. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has provided guidelines that distinguish between the decimal prefixes (like kilo- for 1,000) and the binary prefixes (like kibi- for 2^10), although in common usage, kilobyte often refers to 1,024 bytes. This nuances underscore the complexity and the evolving nature of data size conversions.
Conversion Methods
The exact conversion factor between kilobytes and megabytes is based on the binary system, where 1 megabyte equals 1,024 kilobytes. This conversion factor can be used in multiple calculation methods. For a straightforward conversion, one can simply divide the number of kilobytes by 1,024 to find the number of megabytes.
For example, to convert 5,120 kilobytes into megabytes, you would calculate 5,120 KB / 1,024 = 5 MB.
24 MB. This precision is crucial for storage planning and data management.
Approximation techniques are also useful, especially for mental math. Knowing that 1,024 is roughly 1,000, one can approximate conversions by using the decimal system for quick estimates, though this method may not be suitable for applications requiring high precision.
Understanding when precision matters versus when approximations are acceptable is key. In software development, precise calculations are critical, whereas in casual discussions about file sizes, approximations may suffice. Common conversion mistakes to avoid include confusing binary and decimal prefixes or not accounting for the base-2 nature of digital storage.
Mental math shortcuts, such as recognizing that 1 megabyte is just over 1,000 kilobytes, can facilitate quick conversions in everyday situations. However, for technical applications, relying on the exact conversion factor ensures accuracy and avoids potential issues stemming from imprecision.
Practical Applications
In computer storage, understanding kilobyte to megabyte conversions is essential for managing hard drive space, planning for future storage needs, and optimizing data transfer speeds. 66 MB) helps in determining the required storage capacity.
Network bandwidth is another critical area where these conversions apply. When downloading a file, knowing its size in megabytes and the network speed in megabits per second (Mbps) helps estimate the download time. For example, downloading a 500-megabyte file over a 100 Mbps connection would take approximately 40 seconds, considering 1 megabyte is roughly 8 megabits.
File compression software relies heavily on accurate data size conversions to quantify the compression ratio and the resulting file size. This is crucial for optimizing storage and transfer of compressed files, where even small discrepancies in file size calculations can impact overall system performance.
Backup planning involves similar considerations, as determining the total data size in megabytes helps in choosing appropriate backup media and estimating the time required for backup operations. For example, backing up 10 gigabytes (approximately 10,485 megabytes) of data would require a significant amount of time and storage space, depending on the backup method and medium used.
In software development, understanding data sizes is vital for optimizing code, managing memory allocation, and ensuring that applications run efficiently within the available resources. Digital media services, such as streaming platforms, rely on precise data size conversions to manage content delivery, ensure smooth playback, and optimize user experience based on available bandwidth and device storage capabilities.
Kilobytes to Megabytes Conversion Chart