Days to Weeks Calculator
VerifiedEasily convert days to weeks with our detailed guide and examples
Time Calculator
Convert between different time units instantly with precise calculations
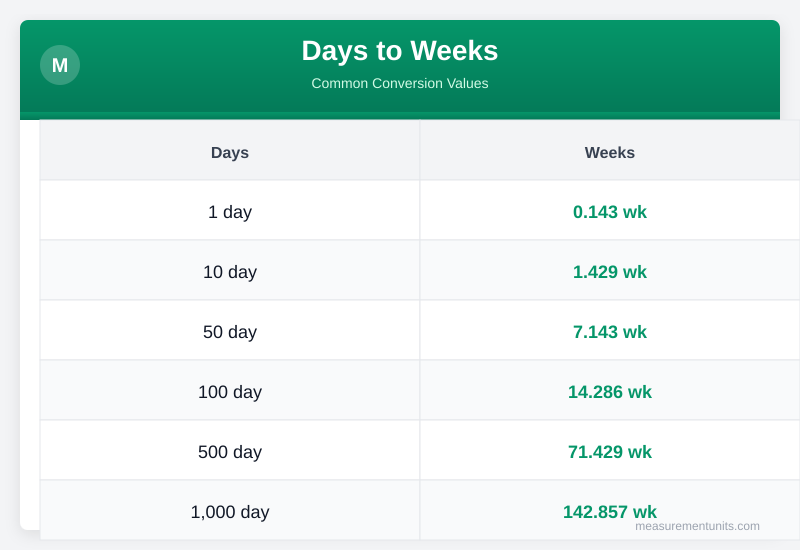
Days to Weeks Conversion Table
Common Days to Weeks conversion values
| Days | Weeks |
|---|---|
| 1 day | 0.143 wk |
| 10 day | 1.429 wk |
| 50 day | 7.143 wk |
| 100 day | 14.286 wk |
| 500 day | 71.429 wk |
| 1000 day | 142.857 wk |
About Days to Weeks Conversion
Got a measurement in Day and need it in Week? The calculator above handles it instantly. We also explain the formula if you're curious.
The measurement of time has a rich history that spans thousands of years, with various systems developed to divide the day into smaller, more manageable units. One of the most widely used time units is the day, which is defined as the period of time it takes the Earth to rotate once on its axis. In contrast, a week is a period of seven days, originating from ancient civilizations who divided the month into four weeks.
The conversion from days to weeks is a fundamental calculation in many applications, including project management, scientific research, and international coordination.
The decimal system, used for metric units, and the sexagesimal system, inherited from Babylonian mathematics, are two primary methods of dividing time. The sexagesimal system, which divides the day into 24 hours, each hour into 60 minutes, and each minute into 60 seconds, is the basis for modern timekeeping. This system was chosen for its ease of calculation and because 60 has many factors, making it a convenient choice for fractional divisions of the day.
However, for some calculations, especially those involving large time spans, converting between days and weeks can simplify planning and scheduling.
Practical applications of converting days to weeks are numerous. In project management, expressing deadlines in weeks can provide a clearer overview of project timelines, especially for tasks that span several months. In scientific research, experiments or observations that run over several weeks can be more easily scheduled and analyzed by converting the total days into weeks.
International coordination across different time zones also benefits from converting days to weeks, as it helps in planning meetings, conferences, and collaborative projects that span across the globe.
The precision required for time conversions varies depending on the context. For everyday planning, converting days to weeks can often be approximated without significant loss of accuracy. However, in scientific calculations, such as astronomy or particle physics, precise time measurements are crucial.
, the exact number of days) will determine the precision of the result.
Understanding the history and rationale behind different time measurement systems can provide insights into why conversions like days to weeks are necessary. The coexistence of decimal and sexagesimal systems is a testament to the evolution of human understanding of time and the need for flexible and adaptable measurement systems. As our ability to measure time with greater precision improves, so does our need to convert between different units of time to accommodate various applications and contexts.
Conversion Methods
The exact conversion factor between days and weeks is straightforward: 1 week equals 7 days. This means that to convert days to weeks, you simply divide the number of days by 7. For example, to convert 28 days into weeks, you divide 28 by 7, which equals 4 weeks.
This calculation is exact and does not require any approximation.
There are multiple methods to perform this conversion, including manual calculation, using a calculator, or employing conversion software. For manual calculations, the division method is the most straightforward. For example, if you want to convert 35 days into weeks, you would divide 35 by 7, which gives you 5 weeks.
If there is a remainder, it represents the additional days beyond complete weeks. In this case, 35 divided by 7 equals 5 with a remainder of 0, meaning 35 days is exactly 5 weeks.
Step-by-step examples can illustrate the conversion process more clearly. Suppose you need to convert 42 days into weeks. First, you divide 42 by 7, which equals 6.
This means 42 days is exactly 6 weeks, with no remainder. If you were converting 43 days, dividing 43 by 7 gives you 6 with a remainder of 1, meaning 43 days is 6 weeks and 1 day.
Approximation techniques can be useful for quick mental math. 3), you can estimate that 30 days is around 4 weeks. However, for precise calculations, especially in scientific or technical contexts, using the exact conversion factor is essential.
Mental math shortcuts can also facilitate quick conversions. For example, to quickly convert days to weeks, you can first divide the number of days by 10 (since 10 is close to 7 and easier to divide by mentally), which gives you an approximation, and then adjust by considering the remaining days. However, this method is less precise and should be used only for rough estimates.
It's crucial to understand when precision matters versus when approximations are sufficient. 2 weeks might be sufficient. However, in engineering, physics, or scheduling critical missions, precise time measurements are vital, and exact conversions are necessary.
Common conversion mistakes to avoid include rounding incorrectly or forgetting to account for the remainder in division. For example, if converting 38 days to weeks, dividing 38 by 7 gives 5 with a remainder of 3, meaning 38 days is 5 weeks and 3 days. Failing to include the remainder (3 days) would result in an incomplete conversion.
Practical Applications
In project management, converting days to weeks is essential for creating realistic timelines and schedules. By breaking down large projects into smaller, week-long tasks, managers can better allocate resources and track progress. 86 weeks) helps in planning and scheduling resources over nearly 13 weeks.
Scientific calculations often require precise time measurements. In astronomy, the observation of celestial events or the planning of space missions depends on accurate time conversions. 14 weeks) can help in planning the countdown and pre-launch preparations.
International coordination across different time zones requires careful consideration of time conversions. For meetings or conferences that involve participants from around the world, converting days to weeks can help in planning and ensuring that all parties are on the same schedule. 57 weeks) can help in planning and reminding participants who are in different time zones.
Transportation scheduling, especially for freight or passenger services that span over several days, benefits from converting days to weeks. 29 weeks), facilitating scheduling and resource allocation.
Historical studies also benefit from converting days to weeks, particularly when analyzing events or trends over long periods. By converting historical time spans into weeks, researchers can gain a better understanding of the pace and progression of historical events. 57 weeks) can provide insights into the labor and resources dedicated to its construction.
Days to Weeks Conversion Chart