Hertz to Revolutions per Minute Calculator
VerifiedConvert frequency from Hertz to RPM with precision, learn about wave physics and applications in electronics, engineering, and more
Frequency Calculator
Convert between different frequency units instantly with precise calculations
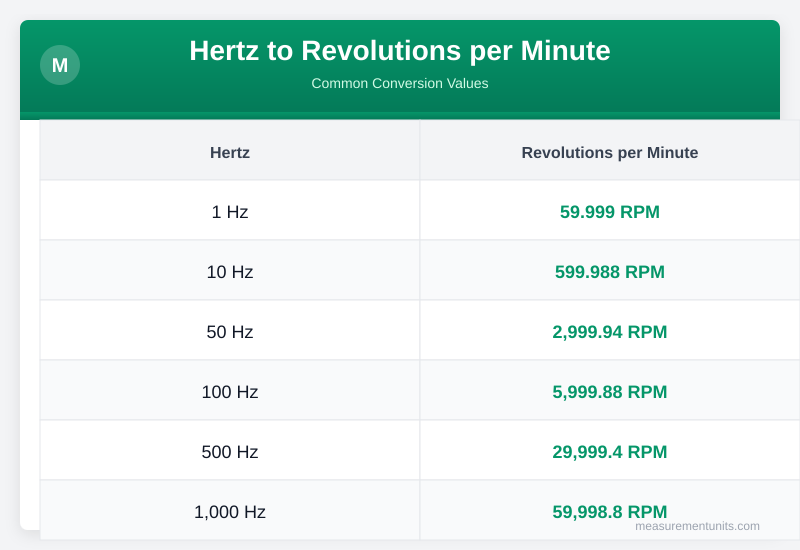
Hertz to Revolutions per Minute Conversion Table
Common Hertz to Revolutions per Minute conversion values
| Hertz | Revolutions per Minute |
|---|---|
| 1 Hz | 59.999 RPM |
| 10 Hz | 599.988 RPM |
| 50 Hz | 2999.940 RPM |
| 100 Hz | 5999.880 RPM |
| 500 Hz | 29999.400 RPM |
| 1000 Hz | 59998.800 RPM |
About Hertz to Revolutions per Minute Conversion
Hertz and Rpm measure the same thing differently. This tool bridges the gap so you don't have to do the math yourself.
The concept of frequency measurement has undergone significant development since the discovery of wave physics. Historically, frequency was first measured in terms of cycles per second, with the term 'Hertz' being adopted in the late 19th century in honor of Heinrich Hertz, a pioneer in the field of electromagnetism. Today, frequency is a fundamental unit of measurement in various fields, including electrical and mechanical engineering, telecommunications, and audio engineering.
In wave physics, frequency is defined as the number of oscillations or cycles per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). The relationship between frequency and rotational speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), is crucial in various applications. For instance, in electrical engineering, the frequency of an alternating current (AC) is related to the rotational speed of the generator or motor.
A typical example is a 50 Hz AC power supply, which corresponds to a rotational speed of 3000 RPM in a synchronous generator.
The conversion from Hertz to RPM is essential in mechanical engineering, particularly in the design and operation of rotating machinery such as engines, pumps, and gearboxes. The rotational speed of these machines is critical to their performance, efficiency, and lifespan. For example, a car engine operating at 6000 RPM has a corresponding frequency of 100 Hz, which is used to tune the engine's ignition and fuel injection systems.
Precision requirements for Hertz to RPM conversions vary depending on the application. In some cases, such as in medical equipment or scientific instruments, high precision is required to ensure accurate measurements and reliable operation. In other cases, such as in audio engineering, a certain degree of tolerance may be acceptable.
Understanding the context and requirements of the conversion is crucial to selecting the appropriate method and level of precision.
The historical context of frequency measurement is closely tied to the development of modern technology. The discovery of the relationship between frequency and rotational speed has enabled the creation of efficient and reliable machinery, which has transformed industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and energy generation. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of accurate frequency measurement and conversion will only continue to grow.
Conversion Methods
The exact conversion factor from Hertz to RPM is 60, since there are 60 seconds in a minute. This means that 1 Hz is equivalent to 60 RPM. To convert a frequency from Hertz to RPM, you can use the following formula: RPM = Hz x 60.
For example, to convert 25 Hz to RPM, you would calculate: RPM = 25 Hz x 60 = 1500 RPM.
There are multiple calculation methods for converting Hertz to RPM, including using online conversion tools, calculators, or software. Alternatively, you can use approximation techniques, such as mental math shortcuts, to estimate the conversion. For instance, you can use the fact that 1 Hz is approximately equal to 60 RPM to make rough estimates.
However, it is essential to note that these approximations may not be suitable for all applications, particularly those requiring high precision.
To illustrate the conversion process, let's consider a few examples. Suppose we want to convert 50 Hz to RPM. Using the exact conversion factor, we get: RPM = 50 Hz x 60 = 3000 RPM.
Another example is converting 120 Hz to RPM, which yields: RPM = 120 Hz x 60 = 7200 RPM. These examples demonstrate the simplicity and accuracy of the conversion process.
When precision matters, it is essential to avoid common conversion mistakes, such as using incorrect conversion factors or neglecting to account for units. For instance, if you forget to multiply the frequency by 60, you may end up with an incorrect RPM value. To ensure accurate conversions, it is crucial to double-check your calculations and verify the units of measurement.
In some cases, approximations may be sufficient, particularly when working with rough estimates or approximate values. However, in applications where precision is critical, such as in medical equipment or scientific instruments, exact conversions are essential. Understanding the context and requirements of the conversion is vital to selecting the appropriate method and level of precision.
Practical Applications
The conversion from Hertz to RPM has numerous applications in various fields, including electronics, telecommunications, and audio engineering. In electronics, the frequency of an alternating current (AC) is related to the rotational speed of the generator or motor. For example, a 50 Hz AC power supply corresponds to a rotational speed of 3000 RPM in a synchronous generator.
In telecommunications, the conversion from Hertz to RPM is used in the design and operation of radio frequency (RF) systems, such as cellular networks and satellite communications. The frequency of the RF signal is related to the rotational speed of the antenna or transmitter, which must be precisely controlled to ensure reliable communication.
In audio engineering, the conversion from Hertz to RPM is used in the design and operation of audio equipment, such as turntables and CD players. The rotational speed of the turntable or disc is critical to the playback quality of the audio signal, and precise control of the RPM is necessary to ensure accurate sound reproduction.
In medical equipment, the conversion from Hertz to RPM is used in the design and operation of medical devices, such as MRI machines and ultrasound equipment. The frequency of the magnetic field or ultrasound signal is related to the rotational speed of the machine, which must be precisely controlled to ensure accurate imaging and diagnosis.
In scientific instruments, the conversion from Hertz to RPM is used in the design and operation of instruments, such as spectrometers and interferometers. The frequency of the light or other signal is related to the rotational speed of the instrument, which must be precisely controlled to ensure accurate measurements and reliable operation.
Hertz to Revolutions per Minute Conversion Chart