Meters to Feet Calculator
VerifiedConvert meters to feet accurately with our comprehensive guide and converter tool
Length Calculator
Convert between different length units instantly with precise calculations
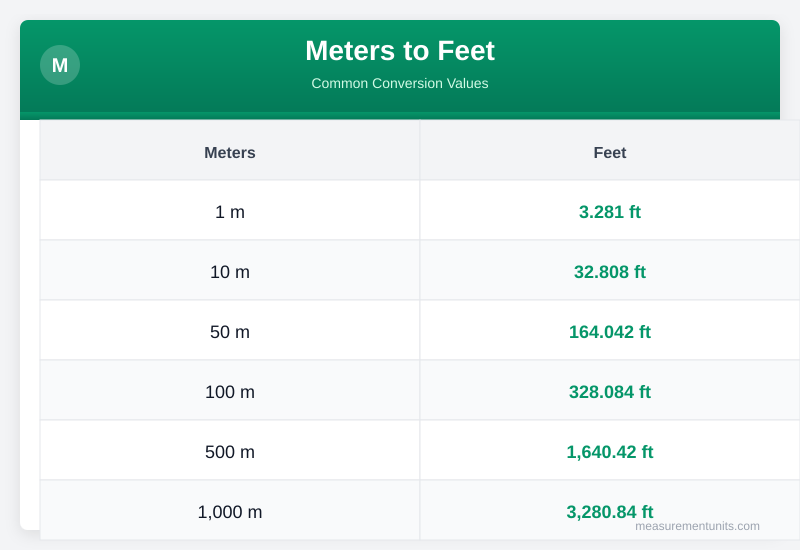
Meters to Feet Conversion Table
Common Meters to Feet conversion values
| Meters | Feet |
|---|---|
| 1 m | 3.281 ft |
| 10 m | 32.808 ft |
| 50 m | 164.042 ft |
| 100 m | 328.084 ft |
| 500 m | 1640.420 ft |
| 1000 m | 3280.840 ft |
About Meters to Feet Conversion
Meter to Foot conversion is straightforward with the right tool. Enter your number above, or read on to learn how the math works.
The meter and foot are two fundamental units of length used in the metric and imperial systems, respectively. The metric system, developed during the French Revolution, is based on the decimal system, with the meter defined as the distance traveled by light in a vacuum in 1/299,792,458 of a second. In contrast, the imperial system, inherited from the British Empire, uses the foot as a unit of length, with 1 foot equal to 12 inches.
Understanding the origins of these systems is crucial for accurate conversions.
The scientific basis of the meter lies in its definition, which is rooted in the speed of light, a universal constant. This definition ensures that the meter remains a consistent unit of measurement across different environments and applications. Conversely, the foot is based on the length of a human foot, which can vary significantly.
This variance highlights the importance of using standardized units like the meter for scientific and technical applications.
Converting meters to feet is essential globally due to the widespread use of both systems. In construction and architecture, for instance, building plans may be drawn in meters, while the materials may be measured in feet. Similarly, in sports and athletics, track and field events are typically measured in meters, while American football fields are measured in feet and yards.
Accurate conversions are vital to avoid errors and ensure consistency.
Common measurement scenarios where meter to foot conversions are necessary include construction projects, where buildings and bridges are designed and built using precise measurements. 09 meters). In such cases, accurate conversions are critical to avoid costly mistakes.
Precision and rounding considerations are also crucial when converting meters to feet. 8084 feet. 81 feet or even 33 feet, depending on the context and required precision.
Understanding the implications of rounding and precision is essential for accurate conversions and real-world applications.
Conversion Methods
2808399 feet. This factor can be used to convert meters to feet by multiplying the number of meters by the conversion factor. 4042 feet.
There are multiple calculation methods for converting meters to feet, including using a calculator, conversion charts, or online tools. For instance, a conversion chart can be used to quickly look up the equivalent value in feet for a given number of meters. Online tools, such as conversion calculators, can also provide accurate conversions with minimal effort.
Step-by-step examples can illustrate the conversion process. 617798 feet). 62 feet.
Approximation techniques can also be used for quick conversions. 3 feet, 10 meters can be approximated as 33 feet. While this method is less accurate, it can be useful for mental math and rough estimates.
Mental math shortcuts can also facilitate conversions. 5 feet. This method provides a quick and reasonably accurate estimate.
When precision matters, exact conversions should be used. For example, in engineering projects, precise measurements are critical to ensure the structural integrity and safety of buildings and bridges. In such cases, using the exact conversion factor and avoiding rounding errors is essential.
Common conversion mistakes to avoid include using incorrect conversion factors, rounding prematurely, and neglecting to consider the context of the conversion. For instance, using an outdated or incorrect conversion factor can result in significant errors, while rounding prematurely can lead to loss of precision.
Practical Applications
In construction and architecture, accurate conversions between meters and feet are crucial for ensuring consistency and avoiding errors. For example, a building's blueprints may be drawn in meters, while the materials, such as lumber and steel, are measured in feet. Converting between these units accurately is essential for successful project execution.
In sports and athletics, precise measurements are necessary for track and field events, such as the 100-meter dash. However, American football fields are measured in feet and yards, highlighting the need for conversions. 44 meters) long, and converting between these units accurately is essential for gameplay and strategy.
International trade relies heavily on accurate conversions, as products are often measured and specified in different units. For example, a shipment of goods may be measured in cubic meters, while the shipping container is measured in cubic feet. Converting between these units accurately is essential for calculating volumes, weights, and costs.
Engineering projects, such as bridge construction, require precise conversions to ensure structural integrity and safety. , 50 meters), while the materials, such as steel and concrete, are measured in feet. Converting between these units accurately is essential for successful project execution.
In real estate, accurate conversions are necessary for measuring property boundaries, room sizes, and building dimensions. 9 square meters. Converting between these units accurately is essential for buyers, sellers, and real estate agents.
Travel and navigation also rely on accurate conversions, as distances and speeds are often measured in different units. 14 miles or 100,000 meters), while a GPS device may display the distance in feet or miles. Converting between these units accurately is essential for navigation and route planning.
Scientific research, such as climate modeling and atmospheric studies, relies heavily on precise conversions between units. For instance, atmospheric pressure may be measured in millibars (mb) or inches of mercury (inHg), while temperature may be measured in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F). Converting between these units accurately is essential for understanding and predicting complex phenomena.
Meters to Feet Conversion Chart